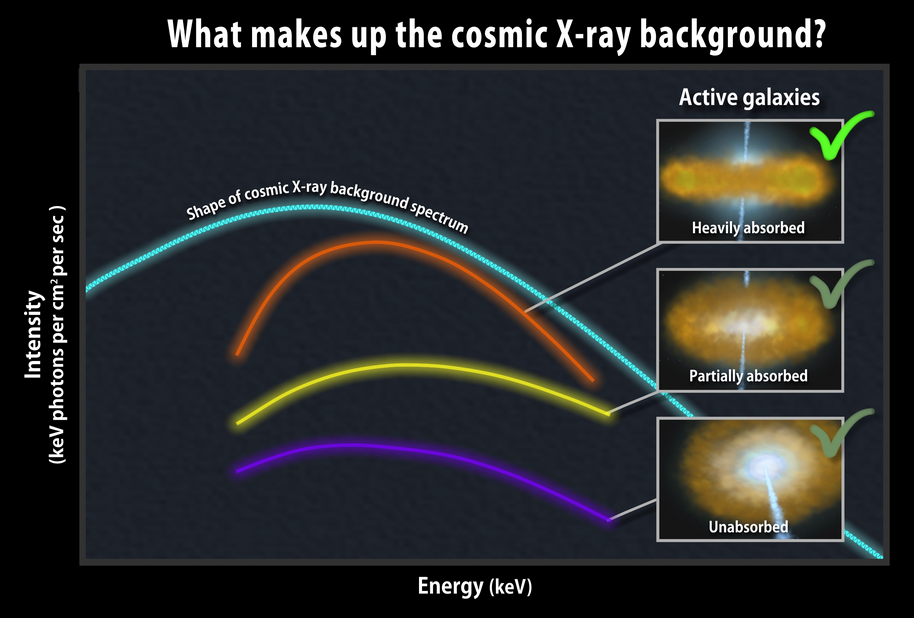
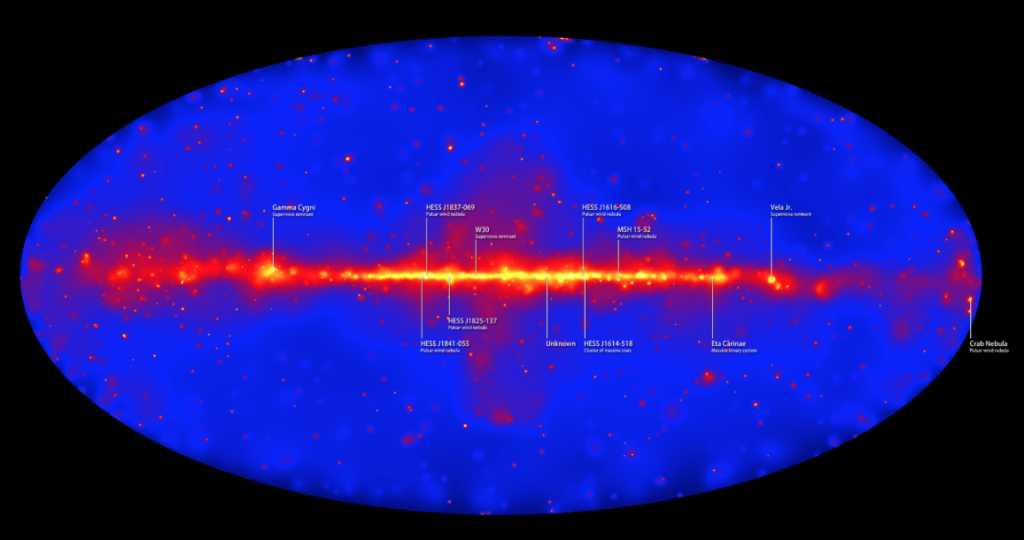
Astronomers studying two classes of black-hole-powered galaxies monitored by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope have found evidence that they represent different sides of the same cosmic coin. By unraveling how these objects, called blazars, are distributed throughout the universe, the scientists suggest that apparently distinctive properties defining each class more likely reflect a change in the way the galaxies extract energy from their central black holes.
“We can think of one blazar class as a gas-guzzling car and the other as an energy-efficient electric vehicle,” said lead researcher Marco Ajello, an astrophysicist at Clemson University in South Carolina. “Our results suggest that we’re actually seeing hybrids, which tap into the energy of their black holes in different ways as they age.”
Read more at NASA’s website.